1 上海理工大学 光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所 高功率激光物理联合实验室,上海 201800
光学元件的损伤在高功率激光系统的终端光学组件中较为普遍且对激光系统的正常运行有重大影响。为提高元件的使用寿命和保证激光光路正常运行,首先要做的是检测和判断出损伤出现的位置、大小、类型。在线检测中终端光学损伤检测装置是一种重要的方法,它能够直接、实时地对元件的损伤情况进行成像并分析,另外还有一种间接获取损伤图像的方式,即用衍射环检测损伤,通过相关公式求出损伤点的大小和位置。针对更小的损伤的检测,深度学习这一工具能够处理大量数据,是目前研究该问题不可或缺的一类方法,它能够减少人工,并提高效率和准确率。修复损伤的主要方式是快速熔融缓解,即二氧化碳激光熔融损伤区,该方法是目前最常见、最有效的修复方式。对损伤问题处理的前提和关键在于精确定位更小的损伤点并分类不同类型的损伤,以便确定后续修复步骤。损伤的检测和修复是光学循环回路策略的重要部分,传统方法有一定的局限性。近些年,受到深度学习在图像处理和目标识别领域的优势的影响,未来会有越来越多深度学习的方法能够被用在与损伤检测相关的研究上。这对高功率激光系统长期稳定运行和正常发展有重要意义和作用。
元件损伤 在线检测 高功率激光系统 损伤修复 深度学习 Element damage On-line inspection High power laser system Damage repair Deep learning 光子学报
2022, 51(10): 1012002

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100094, China
4 e-mail: liudean@siom.ac.cn
5 e-mail: oyxp@siom.ac.cn
A spectrum series learning-based model is presented for mode-locked fiber laser state searching and switching. The mode-locked operation search policy is obtained by our proposed algorithm that combines deep reinforcement learning and long short-term memory networks. Numerical simulations show that the dynamic features of the laser cavity can be obtained from spectrum series. Compared with the traditional evolutionary search algorithm that only uses the current state, this model greatly improves the efficiency of the mode-locked search. The switch of the mode-locked state is realized by a predictive neural network that controls the pump power. In the experiments, the proposed algorithm uses an average of only 690 ms to obtain a stable mode-locked state, which is one order of magnitude less than that of the traditional method. The maximum number of search steps in the algorithm is 47 in the 16°C–30°C temperature environment. The pump power prediction error is less than 2 mW, which ensures precise laser locking on multiple operating states. This proposed technique paves the way for a variety of optical systems that require fast and robust control.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(6): 06001491
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
激光辐照靶面产生的后向受激布里渊散射(SBS)光经连续相位板(CPP)调制会产生衍射强值并对光学元件造成损伤。利用建立的SBS激光后向近场衍射传输模型及菲涅耳衍射理论,分析并数值模拟了衍射距离、CPP设计参数和应用位置等参量对近场衍射调制的影响。结果表明:在一定范围内,近场调制度随衍射距离的增大而迅速增强;CPP相位幅度、最小空间周期和频谱控制均会影响近场调制,其中相位幅度的影响较大;倍频CPP对近场调制的影响小于基频CPP对近场调制的影响。CPP后向近场衍射传输分析有助于理解相位型光学器件的近场光强分布,对高功率激光系统中光学元件的排布及CPP的优化具有指导意义。
衍射 连续相位板 受激布里渊散射 近场调制 惯性约束聚变 光学学报
2020, 40(22): 2205001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
提出了一种基于电光效应的新型光参量放大方案,理论分析了磷酸二氘钾(DKDP)晶体增益带宽随氘化率的变化特性,研究了70%和95%氘化率的DKDP晶体在不同电场强度下的增益带宽变化特性。在885 nm中心波长处,对70%氘化率的DKDP晶体施加大小为1.67×10 5 V/m的场强时,增益带宽可从90 nm拓宽至124 nm;在808 nm中心波长处,对95%氘化率的DKDP晶体施加大小为1×10 5 V/m的场强时,增益带宽可从52 nm拓宽至68 nm。结果表明,在光学参量放大系统中,通过线性电光效应可以有效拓宽系统的增益带宽,同时可通过电光调制调节增益谱的中心波长,以进行连续波长调谐,在高能超短激光系统中具有很大的应用前景。
非线性光学 磷酸二氘钾晶体 宽带光参量放大 电光效应 增益带宽 中国激光
2020, 47(10): 1008001
1 上海大学通信与信息工程学院特种光纤与光接入网省部级共建国家重点实验室培育基地, 上海 200444
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
3 中国科学院大学材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
为实现高灵敏度的外差相位检测,提出了一种基于光外差检测原理的光纤四通道双平衡外差相位检测方法。搭建光纤四通道双平衡外差检测光路,采用1/4波片作为相位检测样品,验证分析了光纤四通道双平衡外差相位检测的性能。分析了外差检测中信号调制频率对相位测量结果的影响,结果表明受限于光电接收器件的响应带宽,过高或过低的调制频率均不能有效检测到相位信息。在实验中,最优的信号调制频率范围为 500.5~1550.5 kHz,实际测得的相位均方根为89.1°,标准差为0.3°。在此基础上,分析了双平衡外差干涉中光纤分束比以及耦合透镜的有效接收口径效应对相位检测的影响。当光纤分束比接近1∶1时,得到了较高信噪比下更加精确的检测结果;通过改变耦合透镜的发射角,验证了有效接收口径对接收信号灵敏度的实际影响。
测量 外差检测 四通道双平衡探测 电光调制 相位检测
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
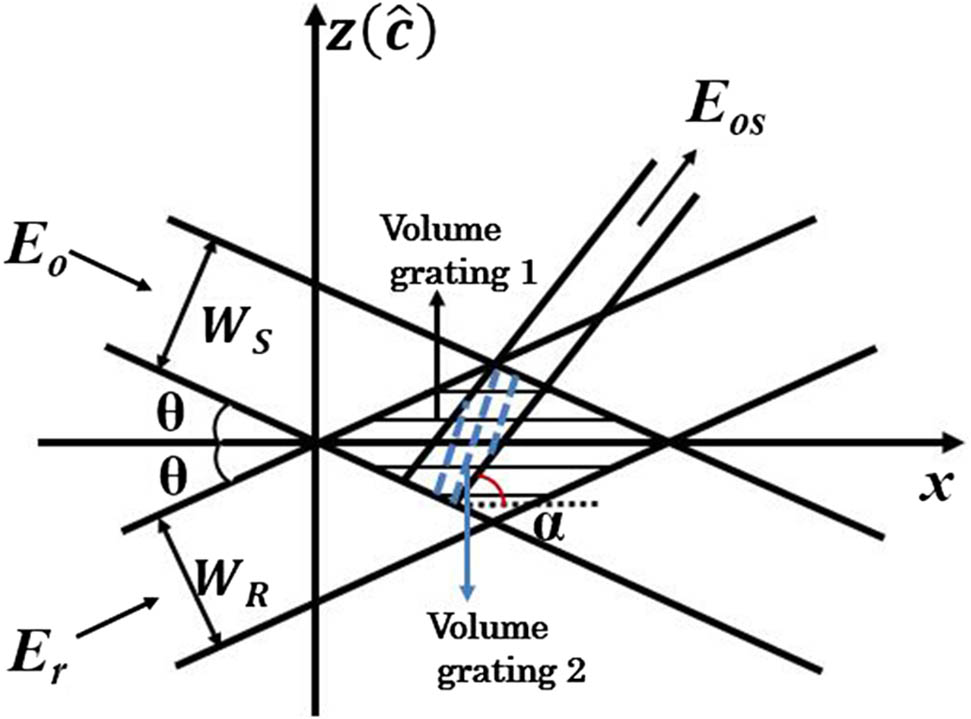
A method is proposed to optimize the recording structure of the photorefractive volume grating to compensate high spatial frequency in the distorted wavefront by optical phase conjugation. Based on the coupled-wave equation, the diffraction efficiency of the recorded grating formed by the scattered beams in different recording structures is simulated. The theoretical results show that the recorded modulations with high spatial frequency can be significantly improved in the small recording angle. In the experiment, three recording structures with the recording angles of 7.5°, 30°, and 45° are chosen to verify the compensation effect. Compared with the reconstructed image in the large recording angle of 45°, the signal to noise ratio of the image recorded at 7.5° increases to 3.2 times of that at 45°.
090.7330 Volume gratings 110.0113 Imaging through turbid media 070.5040 Phase conjugation Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 070901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, Chinese Academy of Engineering and Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
In this paper, we review the status of the multifunctional experimental platform at the National Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics (NLHPLP). The platform, including the SG-II laser facility, SG-II 9th beam, SG-II upgrade (SG-II UP) facility, and SG-II 5 PW facility, is operational and available for interested scientists studying inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and a broad range of high-energy-density physics. These facilities can provide important experimental capabilities by combining different pulse widths of nanosecond, picosecond, and femtosecond scales. In addition, the SG-II UP facility, consisting of a single petawatt system and an eight-beam nanosecond system, is introduced including several laser technologies that have been developed to ensure the performance of the facility. Recent developments of the SG-II 5 PW facility are also presented.
high-power laser facility inertial confinement fusion solid-state amplifier High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(4): 04000e55
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
针对影响高功率激光系统输出性能的空间周期性调制, 提出并分析讨论了一种新的基于相位载波灵活补偿控制的方法。首先, 理论分析了本文方法对空间周期性调制的空间频率的控制, 通过改变相位载波的幅度调节空间频率的强度, 并且对于振幅型周期性调制, 相位载波的周期可以改变空间频率强度极大值的位置。然后, 进行了相位载波对振幅型周期性调制的空间频率影响的实验, 实验结果和数值模拟验证了该方法的可行性, 并对加载相位载波前后的输出近场图及对应的一维平均功率谱密度曲线进行了对比, 加载相位载波后, 空间频率的峰值下降了一个量级, 并降低到了本底值附近。该方法为高功率激光系统中敏感的空间周期性调制的补偿和控制提供了一个新的思路。
物理光学 衍射理论 空间频率 相位载波 空间周期性调制 近场光束 中国激光
2018, 45(10): 1005003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Joint Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
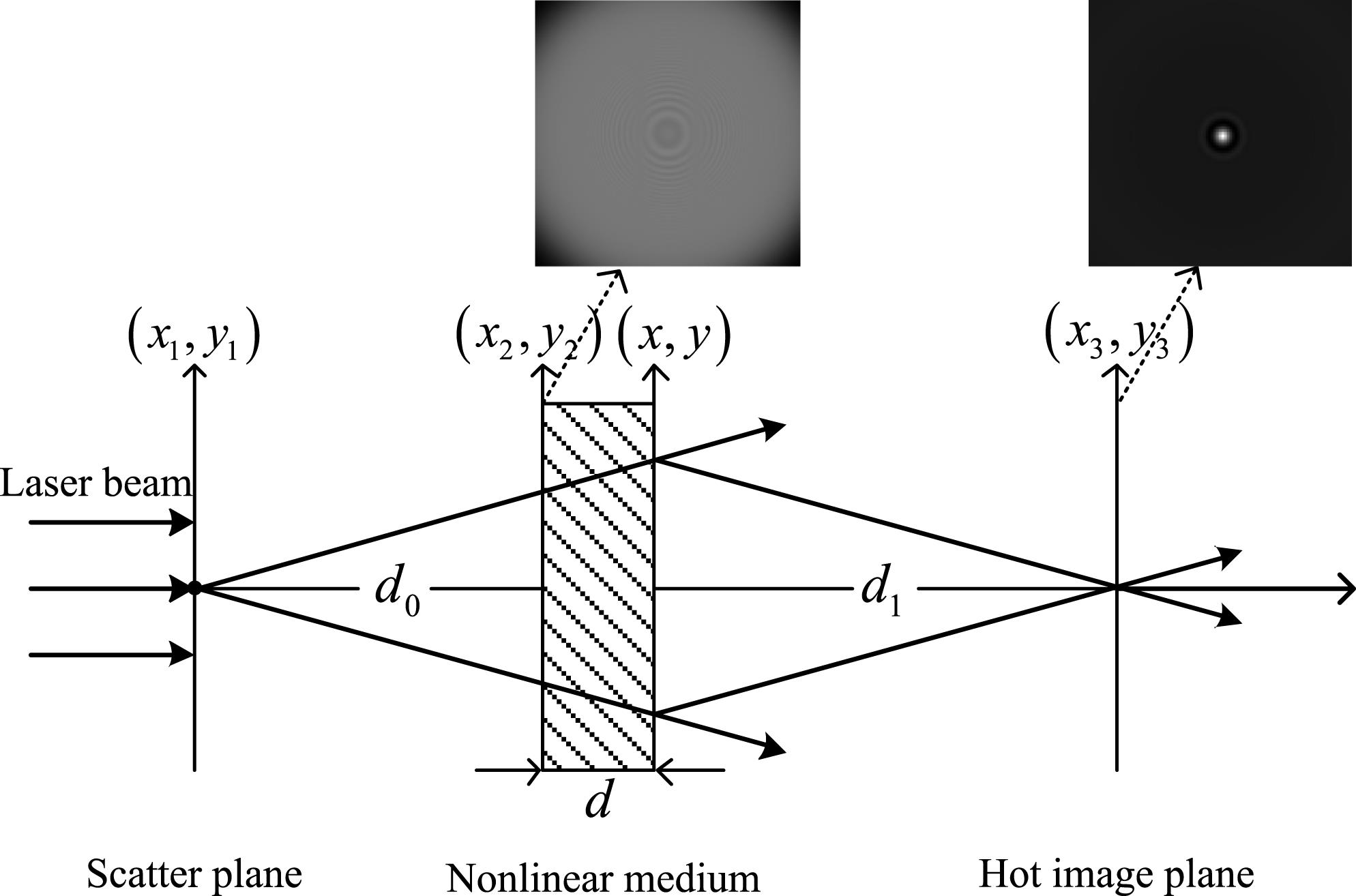
A direct prejudgement strategy that takes the diffraction ring as the analysis target is put forward to predict hot images induced by defects of tens of microns in the main amplifier section of high power laser systems. Analysis of hot-image formation process shows that the hot image can be precisely calculated with the extracted intensity oscillation of the diffraction ring on the front surface of the nonlinear plate. The gradient direction matching (GDM) method is adopted to detect diffraction rings. Recognition of simulated diffraction rings shows that it is feasible to directly prejudge hot images induced by those closely spaced defects and the defects that are far apart from each other. Image compression and cluster analysis are utilized to optimize the performance of the GDM method in recognizing actually collected diffraction images. Results show that hot images induced by defects of tens of microns can be directly prejudged without redundant information.
diffraction rings gradient direction matching method hot images intensity oscillation High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(3): 03000e52
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光物理联合实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
大型高功率激光驱动装置中,激光能量密度及系统运行速度主要受终端光学元件损伤增长的限制。为高效、精确地检测元件的损伤状态,提出了一种基于局部信噪比的自适应差异窗过滤算法。该算法通过设计一种作用在像素点上的窗函数,以关联邻域点的像素值强弱完成目标点或背景点的判断,从而完成种子图像的阈值化,最后通过对种子图像区域生长完成损伤分割。为验证算法的有效性,搭建了在线检测模拟平台以获取损伤样品图像,并使用该算法对图像进行处理。结果表明:对直径50 μm以上的损伤点,算法的平均识别率在99%以上,达到了高功率激光驱动系统对微小损伤检测的精度要求。因其不需要依据经验设定种子图像的阈值,与现有局部信噪比算法相比具有更高的自动化程度。
测量 损伤检测 图像分割 微小尺寸测量 自动检测 区域生长





